
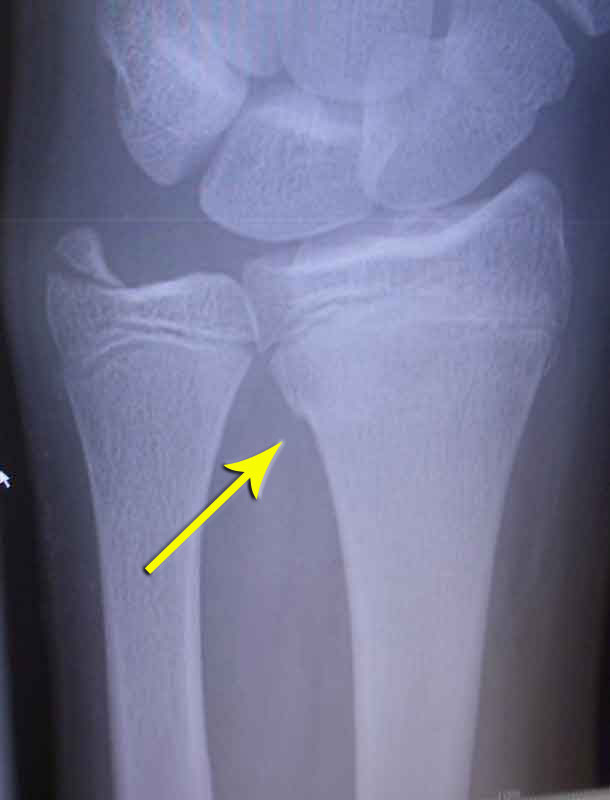
Torus fractures result in a mild deformity without a break in the bone surface, and pain is the main clinical feature.
BUCKLE FRACTURE FULL
Buckle fractures usually require a splint for 3-4 weeks while it heals. It is important to wear the splint for the full time, even after the pain is gone. Such fractures differ from greenstick fractures, in which the bone bends (rather than crushes), resulting in a complete break in one cortex and a bend on the opposite side (akin to snapping a fresh twig from a tree). Your child may have some or all of these symptoms. In long bones, injuries without a cortical break either lead to plastic deformation through microfracture or to a ‘kink’ within the long bone, described as a ‘buckle’ or ‘torus’ fracture. 2 The flexibility of immature bone in children enables force to be absorbed as with the “crumple zone” of a car: crushing-or buckling-as it is injured. 1 They typically occur in children up to age 14, usually after a low energy fall. Torus (buckle) fractures are the most common fractures of the wrist in children, involving the distal radius and/or ulna bone (fig 1). There is no deformity in the wrist, which means the wrist will not be out of its usual shape. The wrist may be tender, slightly swollen, and painful to move. The bone will have a very small fracture, which is so minor that it may be difficult to see on X-ray. Health professionals may consider bandage treatment or even no treatment in the management of this injury, though the safety and acceptability of this approach to patients are not yet known A buckle injury of the wrist is a small area of compressed bone. Splint immobilisation and immediate discharge are recommended in guidelines, such as those from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), however the scientific quality of evidence underpinning the guidelines is rated low or very low the rib) and maintenance of the tensile (outer) side cortex.Evidence suggests that most children with torus fractures of the distal radius make a full recovery within six weeks with no serious problems (including repeat injury) when treated with simple splints History and etymologyīuckle is an engineering term describing cortical disruption to the compressive (inner) side of a structure (i.e. Notice that there is not a fracture line extending across the bone. Arrows point to the buckle in the cortex. As such, the bone is NOT broken into two pieces. On CT, they appear as a focal deformity of the inner cortex or a rib. In a buckle fracture, one or two cortices are compressed during the fall resulting in very slight bending on one side, but the other side of the bone is not injured. Journal of Forensic Sciences Volume: 49 Issue: 6 Dated.

Buckle fractures heal quickly with a splint. Understanding Rib Fracture Patterns: Incomplete and Buckle Fractures. higher energy mechanism more common in younger patients. fall on outstretched hand (FOOSH) is most common in older population. DEXA scan is recommended for women with distal radius fractures. They cannot be detected on routine chest x-ray. A buckle fracture is common injury in children where the bone has not completely broken but has slightly. distal radius fractures are a predictor of subsequent fractures. Radiographic featuresīuckle rib fractures are similar in appearance to buckle fractures elsewhere, but have important implications in forensic radiology. The anterior force responsible for the rib injury may also cause a similar sternal fracture. By definition, a buckle fracture is a stable fracture and stable fractures are less painful than unstable fractures. Thus ribs are not the same as most adult long bones that tend to break like pencils on the tensile side when exposed to an extreme force.īuckle fractures are usually seen in the middle ribs (anterior one-third) and in a line. Pathologyīuckle rib fractures occur in all ages, even very elderly patients. They typically occur due to an anterior compressive force to the chest, most commonly external cardiac massage, but can be seen following any such traumatic injury. the cosmetic and functional prognosis of this fracture is excellent even if it associated with an ulnar buckle/styloid fracture. Buckle rib fractures are incomplete fractures involving only the inner cortex. A Colles fracture is a fracture of the distal metaphysis of the radius with dorsal angulation and displacement leading to a silver fork deformity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
